m-LoRA - How to Efficiently Fine-Tune Dozens of Large Language Models on a Single GPU
Abstract
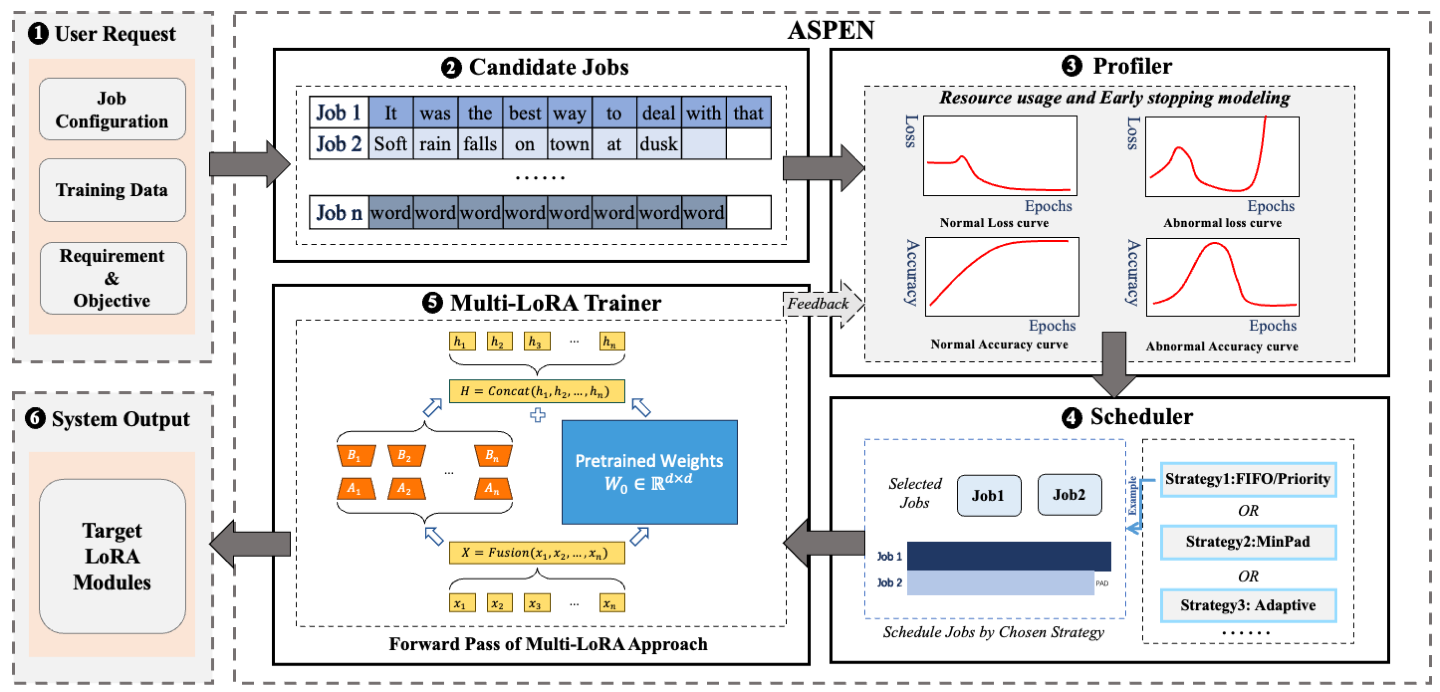
Transformer-based large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated outstanding performance across diverse domains, particularly when fine-turned for specific domains. Recent studies suggest that the resources required for fine-tuning LLMs can be economized through parameter-efficient methods such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA). While LoRA effectively reduces computational burdens and resource demands, it currently supports only a single-job fine-tuning setup. In this paper, we present M-LORA, a high-throughput framework for fine-tuning LLMs. M-LORA efficiently trains multiple jobs on a single GPU using the LoRA method, leveraging shared pre-trained model and adaptive scheduling. M-LORA is compatible with transformer-based language models like LLaMA and ChatGLM, etc. Experiments show that M-LORA saves 53% of GPU memory when training multiple LLaMA7B models on NVIDIA A100 80GB GPU and boosts training throughput by about 17% compared to existing methods when training with various pre-trained models on different GPUs. The adaptive scheduling algorithm reduces turnaround time by 24%, end-to-end training latency by 12%, prioritizing jobs and preventing out-of-memory issues.